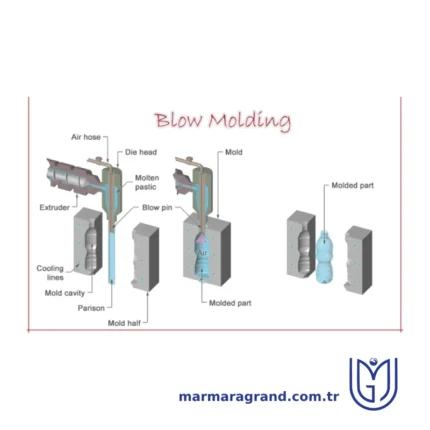
Blow Molding
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts by inflating a heated plastic tube (called a parison or preform) inside a mold cavity until it conforms to the shape of the mold. It is widely used for producing bottles, containers, and other hollow objects.
Types of blow moldingContinuous Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) Process:
- Molten plastic is continuously extruded in a tube-like form (parison).
- A mold clamps around the parison and inflates it with air.
- The part cools and solidifies before being ejected.
- Reciprocating Screw System: The screw moves back and forth to accumulate plastic before pushing it into the mold.
- Accumulator Head System: Plastic is stored in an accumulator before being discharged in a single shot.
- Plastic is first injection molded into a preform (small tube-like shape with a finished neck).
- The preform is then transferred to a blow mold and inflated.
- The final shape is formed, cooled, and ejected.
- Similar to IBM, but includes a stretching step before inflation to improve strength and clarity.
- The preform is reheated, stretched lengthwise, and then blown into shape.
- A parison is extruded and clamped in a mold.
- The parison is stretched both axially (lengthwise) and radially (outward) before being inflated.
Advantages of blow molding
- Cost-Effective Production
- High Efficiency & Fast Production
- Ability to Produce Complex Shapes
- Lightweight and Durable Products
- Versatile Material Usage
- Suitable for Large & Small Products
Disadvantages of blow molding
- Limited to Hollow Shapes
- High Initial Equipment & Mold Costs
- Inconsistent Wall Thickness
- Weak Seams & Stress Points
- Less Precision Compared to Injection Molding
- High Energy Consumption
Applications of blow molding
- packaging Industry: Bottles for beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and household products.
- Automotive Industry: Fuel tanks, air ducts, washer fluid reservoirs, and coolant tanks.
- Industrial & Chemical Storage: Drums, barrels, IBCs, and spray bottles.
- Medical & Pharmaceutical: IV bottles, medicine containers, and diagnostic device housings.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, furniture components, water bottles, and detergent containers.
- Construction Industry: Water tanks, septic tanks, pipes, and conduits.
- Agriculture Industry: Pesticide and fertilizer containers, watering cans, and irrigation components.